---
title: Connect an Elixir application to Neon Postgres
subtitle: Learn how to run SQL queries in Neon from Elixir using Postgrex
enableTableOfContents: true
updatedOn: '2025-09-30T00:26:10.493Z'
---
This guide describes how to create a Neon project and connect to it from an Elixir application using [Postgrex](https://hex.pm/packages/postgrex), a high-performance, concurrent, and robust PostgreSQL driver for Elixir.
You'll learn how to connect to your Neon database from an Elixir application, and perform basic Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations.
## Prerequisites
- A Neon account. If you do not have one, see [Sign up](https://console.neon.tech/signup).
- Elixir v1.12 or later. If you do not have Elixir installed, see the [official installation guide](https://elixir-lang.org/install.html).
## Create a Neon project
If you do not have one already, create a Neon project.
1. Navigate to the [Projects](https://console.neon.tech/app/projects) page in the [Neon Console](https://console.neon.tech).
2. Click **New Project**.
3. Specify your project settings and click **Create Project**.
Your project is created with a ready-to-use database named `neondb`. In the following steps, you will connect to this database from your Elixir application.
## Create an Elixir project
For your Elixir project, create a project directory using `mix` and add the required library.
1. Create a new supervised Elixir project and change into the directory.
```bash
mix new neon_elixir_quickstart --sup
cd neon_elixir_quickstart
```
> Open this directory in your preferred code editor (e.g., VS Code).
2. Add `postgrex` as a dependency in your `mix.exs` file. Find the `deps` function and add `{:postgrex, "~> 0.18.0"}`:
```elixir title="mix.exs"
defp deps do
[
{:postgrex, "~> 0.18.0"}
]
end
```
3. Install the dependency from your terminal:
```bash
mix deps.get
```
## Configure your Neon connection details
You'll configure your application to connect to Neon using the `config/config.exs` file. This method securely separates your credentials from your source code.
1. In the [Neon Console](https://console.neon.tech), select your project on the **Dashboard**.
2. Click **Connect** on your **Project Dashboard** to open the **Connect to your database** modal.
3. Select the **Parameters only** tab to view the connection string parameters.
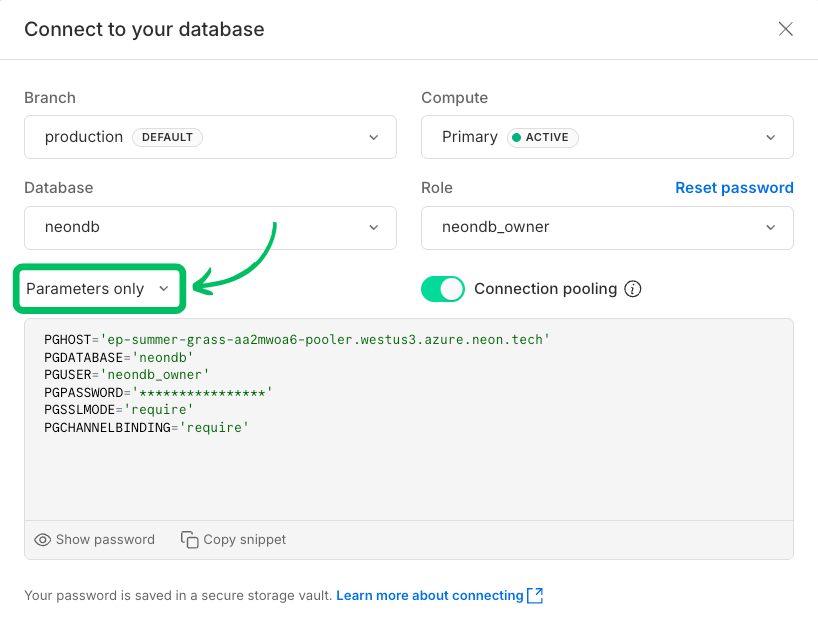
4. Copy the connection string parameters (user, password, host, and database name).
5. Create / Open the `config/config.exs` file and add a configuration block for your project, replacing the placeholder values with your actual database credentials.
```elixir title="config/config.exs"
import Config
config :neon_elixir_quickstart,
username: "[user]",
password: "[password]",
hostname: "[neon_hostname]",
database: "[dbname]",
ssl: [cacerts: :public_key.cacerts_get()]
```
> - The `:ssl` option is required to connect securely to Neon. Using `:public_key.cacerts_get()` tells Postgrex to use the OS-provided CA trust store to verify the server's SSL certificate.
> - The `:neon_elixir_quickstart` key matches your application's name, allowing you to fetch this configuration from your code.
## Examples
This section provides example Elixir scripts that demonstrate how to connect to your Neon database and perform basic operations such as [creating a table](#create-a-table-and-insert-data), [reading data](#read-data), [updating data](#update-data), and [deleting data](#deleting-data).
### Create a table and insert data
In your project's root directory, create a file named `create_table.exs`. This script connects to your Neon database, creates a `books` table, and inserts sample data.
```elixir title="create_table.exs"
defmodule CreateTable do
def run do
# Fetch connection config
config = Application.get_all_env(:neon_elixir_quickstart)
# Start a connection to the database
{:ok, pid} = Postgrex.start_link(config)
IO.puts("Connection established")
try do
# Drop the table if it already exists
Postgrex.query!(pid, "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS books;", [])
IO.puts("Finished dropping table (if it existed).")
# Create a new table
Postgrex.query!(pid, """
CREATE TABLE books (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
author VARCHAR(255),
publication_year INT,
in_stock BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE
);
""", [])
IO.puts("Finished creating table.")
# Insert a single book record
Postgrex.query!(
pid,
"INSERT INTO books (title, author, publication_year, in_stock) VALUES ($1, $2, $3, $4);",
["The Catcher in the Rye", "J.D. Salinger", 1951, true]
)
IO.puts("Inserted a single book.")
# Data to be inserted
books_to_insert = [
{"The Hobbit", "J.R.R. Tolkien", 1937, true},
{"1984", "George Orwell", 1949, true},
{"Dune", "Frank Herbert", 1965, false}
]
# Prepare a statement for efficient multiple inserts
{:ok, statement} = Postgrex.prepare(
pid,
"insert_books",
"INSERT INTO books (title, author, publication_year, in_stock) VALUES ($1, $2, $3, $4);"
)
# Insert multiple books
Enum.each(books_to_insert, fn {title, author, year, stock} ->
Postgrex.execute!(pid, statement, [title, author, year, stock])
end)
IO.puts("Inserted 3 rows of data.")
rescue
e -> IO.inspect(e, label: "An error occurred")
end
end
end
# Run the script
CreateTable.run()
```
The above code does the following:
- Loads the connection configuration from `config/config.exs`.
- Connects to the Neon database using `Postgrex.start_link`.
- Drops the `books` table if it already exists to ensure a clean slate.
- Creates a table named `books` with columns for `id`, `title`, `author`, `publication_year`, and `in_stock`.
- Inserts a single book record using `Postgrex.query!`.
- Uses a prepared statement with `Postgrex.prepare` and `Postgrex.execute!` for efficiently inserting multiple records.
Run the script using the following command:
```bash
mix run create_table.exs
```
When the code runs successfully, it produces the following output:
```text title="Output"
Connection established
Finished dropping table (if it existed).
Finished creating table.
Inserted a single book.
Inserted 3 rows of data.
```
### Read data
In your project directory, create a file named `read_data.exs`. This script connects to your Neon database and retrieves all rows from the `books` table.
```elixir title="read_data.exs"
defmodule ReadData do
def run do
config = Application.get_all_env(:neon_elixir_quickstart)
{:ok, pid} = Postgrex.start_link(config)
IO.puts("Connection established")
try do
# Fetch all rows from the books table
result = Postgrex.query!(pid, "SELECT * FROM books ORDER BY publication_year;", [])
IO.puts("\n--- Book Library ---")
for row <- result.rows do
[id, title, author, year, in_stock] = row
IO.puts(
"ID: #{id}, Title: #{title}, Author: #{author}, Year: #{year}, In Stock: #{in_stock}"
)
end
IO.puts("--------------------\n")
rescue
e -> IO.inspect(e)
end
end
end
ReadData.run()
```
The above code does the following:
- Loads the connection configuration and connects to the database.
- Uses a SQL `SELECT` statement to fetch all rows from the `books` table, ordered by `publication_year`.
- Iterates through the `rows` field of the `Postgrex.Result` struct.
- Prints each book's details in a formatted output.
Run the script using the following command:
```bash
mix run read_data.exs
```
When the code runs successfully, it produces the following output:
```text title="Output"
Connection established
--- Book Library ---
ID: 2, Title: The Hobbit, Author: J.R.R. Tolkien, Year: 1937, In Stock: true
ID: 3, Title: 1984, Author: George Orwell, Year: 1949, In Stock: true
ID: 1, Title: The Catcher in the Rye, Author: J.D. Salinger, Year: 1951, In Stock: true
ID: 4, Title: Dune, Author: Frank Herbert, Year: 1965, In Stock: false
--------------------
```
### Update data
In your project directory, create a file named `update_data.exs`. This script connects to your Neon database and updates the stock status of the book 'Dune' to `true`.
```elixir title="update_data.exs"
defmodule UpdateData do
def run do
config = Application.get_all_env(:neon_elixir_quickstart)
{:ok, pid} = Postgrex.start_link(config)
IO.puts("Connection established")
try do
# Update a data row in the table
Postgrex.query!(pid, "UPDATE books SET in_stock = $1 WHERE title = $2;", [true, "Dune"])
IO.puts("Updated stock status for 'Dune'.")
rescue
e -> IO.inspect(e)
end
end
end
UpdateData.run()
```
The above code does the following:
- Loads the connection configuration and connects to the database.
- Uses a SQL `UPDATE` statement with parameters to change the `in_stock` status of the book 'Dune' to `true`.
Run the script using the following command:
```bash
mix run update_data.exs
```
After running this script, you can run `read_data.exs` again to verify that the row was updated.
```bash
mix run read_data.exs
```
When the code runs successfully, it produces the following output:
```text title="Output"
Connection established
--- Book Library ---
ID: 2, Title: The Hobbit, Author: J.R.R. Tolkien, Year: 1937, In Stock: true
ID: 3, Title: 1984, Author: George Orwell, Year: 1949, In Stock: true
ID: 1, Title: The Catcher in the Rye, Author: J.D. Salinger, Year: 1951, In Stock: true
ID: 4, Title: Dune, Author: Frank Herbert, Year: 1965, In Stock: true
--------------------
```
> You can see that the stock status for 'Dune' has been updated to `true`.
### Delete data
In your project directory, create a file named `delete_data.exs`. This script connects to your Neon database and deletes the book '1984' from the `books` table.
```elixir title="delete_data.exs"
defmodule DeleteData do
def run do
config = Application.get_all_env(:neon_elixir_quickstart)
{:ok, pid} = Postgrex.start_link(config)
IO.puts("Connection established")
try do
# Delete a data row from the table
Postgrex.query!(pid, "DELETE FROM books WHERE title = $1;", ["1984"])
IO.puts("Deleted the book '1984' from the table.")
rescue
e -> IO.inspect(e)
end
end
end
DeleteData.run()
```
The above code does the following:
- Loads the connection configuration and connects to the database.
- Uses a SQL `DELETE` statement to remove the book '1984' from the `books` table.
Run the script using the following command:
```bash
mix run delete_data.exs
```
After running this script, you can run `read_data.exs` again to verify that the row was deleted.
```bash
mix run read_data.exs
```
When the code runs successfully, it produces the following output:
```text title="Output"
Connection established
--- Book Library ---
ID: 2, Title: The Hobbit, Author: J.R.R. Tolkien, Year: 1937, In Stock: true
ID: 1, Title: The Catcher in the Rye, Author: J.D. Salinger, Year: 1951, In Stock: true
ID: 4, Title: Dune, Author: Frank Herbert, Year: 1965, In Stock: true
--------------------
```
> You can see that the book '1984' has been successfully deleted from the `books` table.
## Next steps: Using an ORM or framework
While this guide demonstrates how to connect to Neon using raw SQL queries, for more advanced and maintainable data interactions in your Elixir applications, consider using an Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework. ORMs not only let you work with data as objects but also help manage schema changes through automated migrations keeping your database structure in sync with your application models.
Explore the following resources to learn how to integrate ORMs with Neon:
- [Connect an Elixir Ecto application to Neon](/docs/guides/elixir-ecto)
## Source code
You can find the source code for the application described in this guide on GitHub.
Get started with Elixir and Neon using Postgrex
## Resources
- [Postgrex Documentation](https://hexdocs.pm/postgrex/Postgrex.html)